Towards Interactive Approaches for Information Searching in Mixed Reality
Yiwen Zhang , Xiaohua Sun, Yate Ge,Hexin Zhang,Hang Yu,Zixuan Wang,Qi Wang,Jan Dorning
DVHG DIGEST 2020
摘要/Abstract
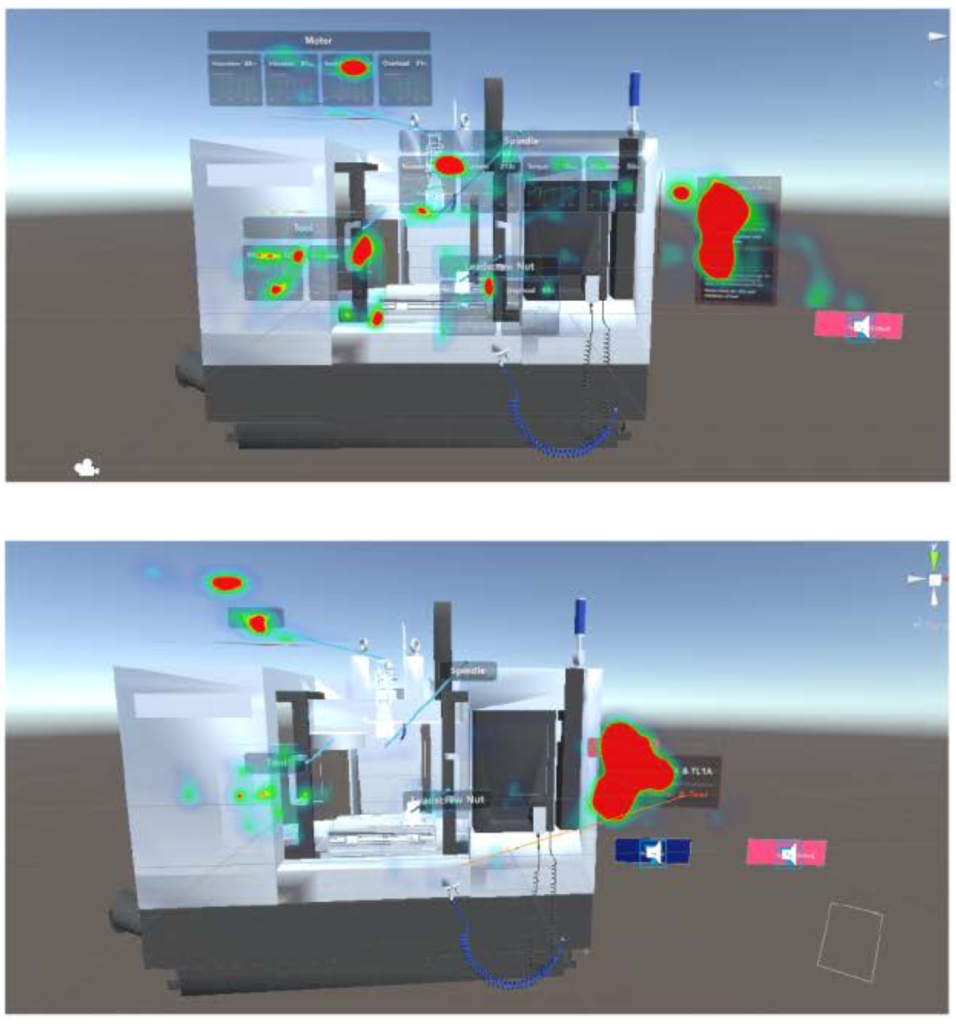
混合现实(MR)设备模糊了虚拟世界与现实之间的界限,重塑了人们使用辅助信息的方式。然而,在 MR 眼镜中执行信息搜索任务时,仍然存在很强的局限性。最近发布的磁共振设备 HoloLens 2 的新增功能为解决这些问题带来了新的可能性。本研究提出了交互式方法,包括身体/手部锁定组件、视图锁定导航组件和视图敏感信息布局。我们开发了使用和不使用这些交互方法的原型,并对用户进行了研究,以衡量任务执行情况、可用性和临场感。结果表明,交互式方法对任务完成时间有积极影响。不同的认知和行为风格可能会导致对不同交互方式的不同偏好。
Mixed reality (MR) devices blur the boundaries between the virtual world and reality, reshaping the way people work with assistive information. However, there are still strong lim-for information searching tasks in MR glasses. Added capabilities of HoloLens 2, a recently released MR device, bring new possibilities to deal with these issues. Interactive approaches are proposed in this study, including body/hand-locked components , view-locked navigation components, and view-sensitive information layout. Prototypes were developed with and without these interactive approaches, and user studies were conducted to measure the task performance, usability, and presence. Results show that interactive approaches have positive effect in terms of task completion time. Different cognitive and behavioral styles may lead to distinct preferences for different interactive approaches.
相关信息/Info
作者/Authors
链接/Link
Yiwen Zhang , Xiaohua Sun, Yate Ge,Hexin Zhang,Hang Yu,Zixuan Wang,Qi Wang,Jan Dorning
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358769033_Towards_Interactive_Approaches_for_Information_Searching_in_Mixed_Reality
